21 Dec 2022
Online Trust & Centralized Databases
Online trust refers to the level of confidence that individuals or organizations have in the reliability, security, and credibility of online platforms, websites, and services. As the internet has become an increasingly integral part of our daily lives, the importance of online trust has grown significantly.
In the early days of the internet, trust was often established through centralized databases and systems that were managed by a single entity or organization. These centralized systems were often seen as more reliable and trustworthy because they were controlled by a single entity, and there was a clear chain of custody for the information they contained. However, this approach also had its drawbacks, as it made the system vulnerable to attacks and breaches, and gave the central authority a great deal of power over the data and information that was stored within it.
Over time, as the internet has evolved and decentralized technologies have emerged, online trust has become more complex. Decentralized systems, such as blockchain, have made it possible for multiple parties to participate in the verification and validation of data, which has increased the level of trust in these systems. In addition, advances in cryptography and secure communication protocols have helped to improve the security and confidentiality of online transactions, further increasing trust in the online environment.
Today, online trust is established through a combination of technical measures, such as encryption and authentication protocols, as well as more intangible factors, such as the reputation and credibility of the parties involved. As the internet continues to evolve and new technologies emerge, the ways in which online trust is established and maintained will undoubtedly continue to change and evolve as well.
Building trust with Confidential Consortium Framework CCF
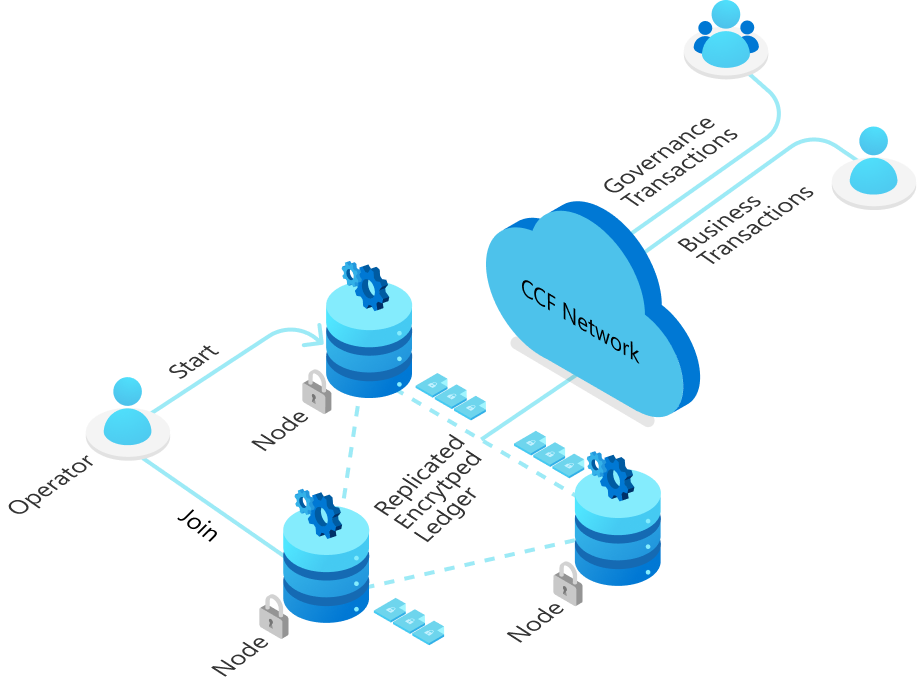
Microsoft Confidential Consortium Framework (CCF) is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology (DLT) platform that is designed to enable organizations to build distributed trust across a network of participants. CCF is based on the open-source Corda platform, which was developed by the Corda consortium and is used by a number of financial institutions and other organizations around the world.
One of the key ways in which CCF helps to build distributed trust is through the use of digital signatures and cryptographic hashes. These tools allow participants in a CCF network to securely and verifiably sign and validate transactions, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and modify the data on the ledger.
In addition, CCF allows for the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts enable parties to automate complex processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, which can help to increase trust and reduce the risk of fraud or errors.
CCF also includes a number of other features that help to build trust within the network, including privacy controls, auditing and compliance tools, and support for multiple consensus algorithms. Overall, CCF is designed to provide a secure, transparent, and scalable platform that enables organizations to build distributed trust and facilitate secure and efficient transactions.
CCF is built on top of the Corda platform, which uses a unique consensus model called "Notary cluster consensus" to enable the secure and verifiable execution of transactions. This model uses a group of trusted notary nodes to validate and timestamp transactions, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and modify the data on the ledger.
In addition to its consensus model, CCF includes a number of other technical features that help to enhance security and trust within the network. These features include:
- Cryptographic hashes: CCF uses cryptographic hashes to securely sign and validate transactions, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and modify the data on the ledger.
- Smart contracts: CCF allows for the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts enable parties to automate complex processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, which can help to increase trust and reduce the risk of fraud or errors.
- Privacy controls: CCF includes privacy controls that enable participants to choose which data they share and with whom they share it, ensuring that sensitive information is kept confidential.
- Auditing and compliance tools: CCF includes a number of auditing and compliance tools that enable organizations to monitor and track their transactions and ensure that they are in compliance with relevant regulations.
Overall, CCF is designed to provide a secure, transparent, and scalable platform that enables organizations to build distributed trust and facilitate secure and efficient transactions.
Ref
Confidential Consortium Framework (microsoft.com)


